Understanding Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatments
Clusters of crystals called kidney stones are created in your urinary tract by minerals and other substances. The majority of stones naturally exit your body through urine, but while they do so, they can cause excruciating discomfort. If the stone get too big to pass through naturally or become an obstruction, you may require an operation to break it up or remove it.
What are the various types of Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are available in an extensive variety of shapes and hues.
>80% Calcium stones.
Kidney stones most commonly occur as calcium stones. Calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate are the two forms of calcium stones. The most prevalent kind of calcium stone is definitely calcium oxalate. Calcium stones are more common in those whose urine contains an excessive amount of calcium. There are various reasons why calcium stones can form in the urine even when there is normal calcium content.
5–10% of stones with uric acid
One waste product that results from chemical reactions within the body is uric acid. Urine that is too acidic for uric acid crystals to breakdown in will result in uric acid stones.
10% of stones have infection or struvite.
Rare yet connected to urinary tract infections, struvite stones develop in alkaline urine as a result of specific microbes. They are big, grow quickly, and branch out frequently. Recurrent UTIs and illnesses that interfere with bladder emptying, such as neurological diseases or paralysis, are risk factors.
Less than 1% of stones are cystine stones.
One of the amino acids that makes up protein is cysteine, which can be found in several meals. An uncommon, inherited metabolic disease is called cystinuria, or having too much cystine in the urine. It occurs when cystine in the urine is not reabsorbable by the kidneys. Urine that contains high levels of cystine might result in stones. Cystine stones frequently begin to develop in childhood.
Causes of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can occur in anyone, although certain individuals are predisposed to them more than others.
• It has been found kidney stones prevalence in India is at 12%, which is similar to prevalence globally.
• Kidney stones are more common in men than in women.
• It is found common among the people aged between 20-50 years
• Additionally, A kidney stone may also be more likely to occur if one had experienced kidney stones,
If anyone who has kidney stones in their family
• Consume insufficient amounts of water
• Consume a lot of sugar, salt, or protein, are overweight,
• If one had intestinal surgery, or if they possess renal polycystic disease,
• If one suffering from a medical condition that results in elevated levels of cystine, oxalate, uric acid, or calcium in your urine or a medical condition that damages or swells your joints, digestive tract, or both , consume specific medications, such as calcium based antacids or diuretics (water pills).
• Hyperparathyroidism : The overproduction of parathyroid hormone by your parathyroid glands can cause an increase in blood and urine calcium levels.
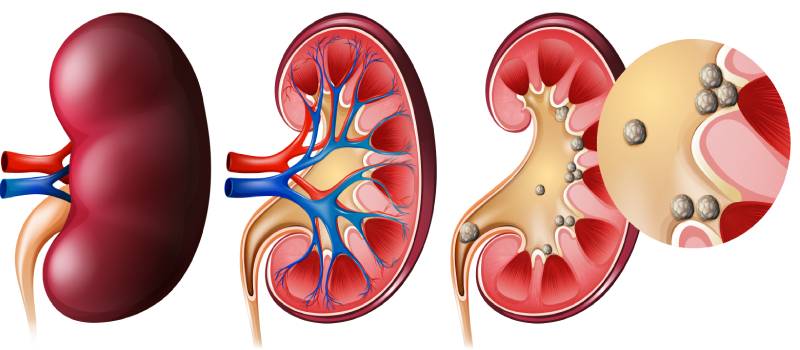
Symptoms
Before the stones pass through the ureters , which are the tubes that allow urine to empty into your bladder, one might not have any symptoms. when this occurs, the kidney’s ability to expel urine may be impeded by the stones.
1.The primary symptom is intense pain that comes on suddenly and goes away, it can occur at the side of the back or the abdomen which tend to hurt, pain may radiate to the labia(women), testicles(men), and groyne area (groyne discomfort).
2.Unusual colour of the urine
3. Blood in urine
4. chills
5. High temperature
6.Vomiting and Nausea
7. Frequent urge to urinate
8. feel as if urine contains pebbles
Diagnosis
To identify kidney stones, medical experts employ tests, a physical examination, and your medical history. Test results may also reveal issues that led to the development of a kidney stone . Following tests help to detect the presence of kidney stone:
• Blood tests: They can determine whether your blood contains excessive levels of uric acid or calcium. They also provide a wealth of information about your kidneys' health to your doctor.
• Urine test: The physician can instruct you to gather one or two samples every 24 hours. It indicates whether there are too many minerals that can form stones in your urine or not enough of other substances that prevent stones from forming.
• Imaging tests: These are used by medical professionals to look for urinary tract stones. An X ray of your abdomen or a CT scan, which creates an image of your body by combining several X rays, may be performed. Larger stones can be seen on an X ray, while smaller stones are easier to find using a CT scan.
• Analysis of passed stones: To collect any stones you may pass, the doctor will have you urinate through a strainer. To find out what they are made of, they will send them to a lab. This can help them diagnose your stones and determine the best course of action.
Treatment:
Pain management: Physicians frequently prescribe nonsteroidal anti inflammatory drugs as a kind of pain relief. Its purpose is to decrease the discomfort brought on by kidney stones moving.
Medical Procedures: Surgery, ureteroscopy, and lithotripsy are often used treatments for kidney stones. Larger stones are removed with them. Shock waves are used in lithotripsy to shatter the stones. During a ureteroscopy, the doctor extracts the stones with a thin tube.
Preventive Actions
Hydration: One should make an effort to continue consuming enough water. Since it will assist you in avoiding the mineral concentration that gives rise to stones.
Dietary Adjustments: Make an effort to adhere to a few diet adjustments, like:
consuming foods high in oxalate in moderation, cutting back on animal protein and salt intake, maintaining a calcium rich diet. Each of these elements will assist you in avoiding the creation of stones.
Medication: To regulate certain chemicals in urine, doctors may in some situations advise taking medication. It helps to keep kidney stones from developing any further.
Frequent Check ups: one should see their doctor for follow ups and routine check ups if they have a history of kidney stones. These operations are carried out to monitor your status on a frequent basis in order to expedite your recovery.
Sri Balaji Action Medical Institute (SBAMI) dedication in providing patients with the best treatment possible makes it stand out as a renowned hospital. It utilises advanced techniques and a multidisciplinary approach to provide individualised care and maximise results.
SBAMI is still at the forefront of kidney stone treatment, giving those who are impacted by this difficult ailment hope and relief.