Understanding PCOD and PCOS: Symptoms, Reasons, Differences, and Treatment.
Ovarian cysts and polycystic ovary disorder are often heard consequences of female health problems. These terms are frequently used interchangeably; there is an ambiguity in their different meanings. In this blog, we are going to investigate the causes, symptoms, and treatment methods of PCOD and PCOS.
In addition, we dive into the key differences between the two conditions so you can pick the right treatment. Most importantly, we discuss why it is so important to tell them apart. Continue reading for the details!
What Is PCOD?
PCOD, as an abbreviation of Polycystic Ovarian Disorder, is one of the common endocrine diseases that mostly occurs among women in reproductive age. It is a small cystic form, which is mostly found in ovaries leading to hormones fluctuation on a wide range of symptoms.
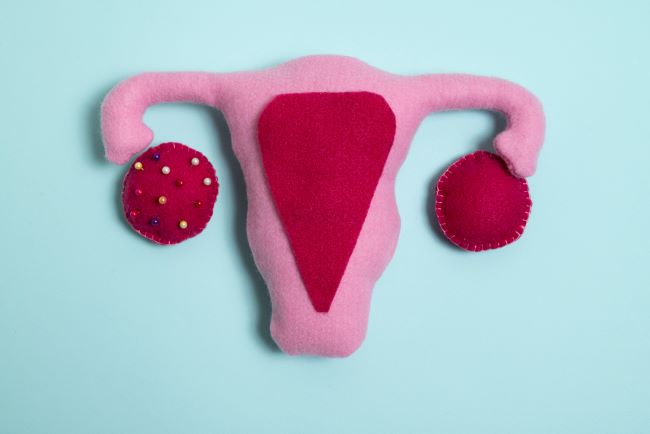

This is also associated with an increased chance of getting type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and coronary heart disease. However, we cannot completely pinpoint the exact cause of PCOD, but it is suspected to be the combination of both genetic and environmental elements.
What Is PCOS?
PCOS is an abbreviation for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. It is a metabolic abnormality that is a problem for many women of reproductive age in the world. PCOS expresses the high rate of androgen and estrogen hormones, raised blood sugar levels, and irregular periods. The unwanted effects of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome involve hirsutism, pimples, and an increased chance of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Proper, timely diagnosis and treatment, like surgery or medication, would be preferable for PCOS, which strikes approximately (1 in 10) women. There is a much higher possibility of ovarian as well as endometrial cancers, yet breast cancer is going to be in patients with PCOS.
Signs and Symptoms Of PCOS And PCOD
Individual reactions may differ, but, judging by the symptoms, they can range from mild to severe. These disease conditions can be occult and a person may not be aware if he/she does not have any symptom that would raise suspicion.
PCOD Symptoms
• Irregular or/ and delayed periods or having no periods at all.
• Heavy menstrual flow.
• Weight gain or weight loss trouble.
• Insulin resistance or diabetes of type 2.
• High blood pressure
• Fatigue
• Excessive hair growth in the face, chest, abdomen, or back may be a common effect.
• Trouble with acne or oiliness
• Mood swings or even symptoms of depression can be caused by menopause.
PCOS Symptoms
• Unpredictable periods (without any particular pattern) or no periods at all.
• Menorrhagia or Heavy bleeding during periods
• The development of obesity or the inability to lose weight.
• Insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
• Hypertension (Affectional pressure on blood)
• Fatigue
• Mood swings or depression
• Sustained abnormally-growth of hairs on the face, chest, stomach or back
• Acne or greasy skin
• Difficulty getting pregnant
• Pelvic pain or discomfort may exist
• Darkenings of skin, most usually around the neck, groin, or underarms.
What Are The Causes Of PCOS And PCOD?
1. Insulin Resistance
A large number of PCOS/PCOD-affected women have insulin resistance, which makes them unresponsive to insulin, which causes hindrance to maintaining blood sugar levels within normal ranges. This may produce an excessive production of androgens (male hormones) because of abnormally high insulin levels in the blood, making an ovarian problem called PCOS or PCOD more possible.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones are the cornerstone of PCOS and PCOD, and their increase or decrease contributes to the key features of these conditions. For example, androgen hormones (male hormones such as testosterone) are high, while levels of progesterone are low. These, in turn, lead to the disruption of the menstrual cycle, to having spots, and to the appearance of other non-pleasing symptoms/signs.
3. Genetics
PCOS and PCOD are largely seen in families with a strong tendency to pass on this disease, which to some extent could have a genetic factor involved in the emergence of this disease.
4. Inflammation
Identical conditions such as chronic inflammation (as a body component factor) increase the likelihood of having PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome) or PCOD (polycystic ovarian pathology).
5. Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, plays a significant role in PCOS and PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Disorders due to Egg-cell) development.
Difference Between PCOD And PCOS
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
| Aspect | PCOD (Polycystic Ovarian Disease) | PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) |
Definition |
PCOD stands for endocrine disorder, where the ovaries contain multiple small ovarian cysts. It is generally linked to irregular menstrual cycles and hormonal imbalances, which again contribute to other health problems. |
PCOS is the abnormal state where the ovaries are highly enlarged, and cysts are found on their edge. It manifests itself by a series of disruptions like irregular periods, high levels of female hormones (androgen) and cysts in the ovaries. |
Hormonal Imbalance |
Endocrine disorders, especially those involving insulin and androgens, are often the culprit. Insulin resistance commonly occurs. |
Hormonal imbalances are often related to the androgens (male hormones), like testosterone, which are at a higher level compared to normal. The patients are usually diagnosed with insulin resistance. |
Symptoms |
Irregular menstrual periods - Difficulty conceiving a baby - Weight gain or general difficulty in losing weight - Acne - Excessively growing hair (hirsutism) - Almost going bald - Hormonal disturbance. |
No regular menstrual cycle or not having menstruation - Infertility - Weight gain or difficulties while losing weight - Acne- too much hair growth (hirsutism)- Hair falling on the scalp - Hormonal disturbances |
Diagnostic Criteria |
The diagnosis is mostly based on ultrasound examination in which multiple cysts are visible in ovaries, and clinical symptoms include irregular periods and hormonal problems as well. |
Diagnosis is carried out by the evaluation of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles and enhanced testosterone levels as well as the presence of ovarian cysts through ultrasound imaging. Hormonal tests, which essentially imply that the level of testosterone is measured, will also be included. |
Management |
|
Management involves life changes like dieting and regular workouts to increase insulin sensitivity, the use of medications to regulate hormones and manage symptoms (for instance, oral contraceptives and anti-androgens), and fertility treatment if infertility is a concern. There is a focus on weight control as well. |
Treatment of PCOD and PCOS.
The therapy for PCOD and PCOS can be different according to the degrees of symptoms presented, age, and any other medical issues a woman may be having. Consequently, care and the advice of the provider prior to the beginning of treatment are crucial. Moreover, the treatment plan should be customised according to each patient’s symptoms and past medical history.
Treatment For PCOD
1. Lifestyle Changes
Consuming a balanced diet rich in whole grains, healthy fats, and lean protein in the right amounts and exercising regularly are the most effective ways to regain control of PCOD.
2. Medications
Hormonal contraceptive pills, Metformin and Clomiphene citrate, which can be prescribed, can be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce symptoms like acne and hirsutism (excess hair growth.)
3. Surgery
In cases when drugs and lifestyle alterations do not resolve symptoms, then ovarian drilling through the laparoscopic route becomes the only option.
Treatment For PCOS
1. Lifestyle Changes
Healthy weight maintenance, eating a balanced diet, and regular exercise are definitely the things that can help you cope with PCOS symptoms.
2. Medications
The menstrual cycle regulation medications, like birth control pills, Metformin, and spironolactone, may be given when needed to a patient to reduce such symptoms as acne and excessive hair growth.
3. Insulin-sensitizing Drugs
These medications offer an advantage over oral meds because they are insulin-sensitizing and thus carry a lesser risk of developing diabetes.
4. Fertility treatments
Assisted reproduction techniques, including artificial Insemination, IVF/ ICSI, or ovulation induction, might be recommended to patients trying to have a child.
Conclusion
PCOD (Polycystic Ovary Disease) and PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) are two hormonal disorders that have two different treatment plans. Timely determination of symptoms and the subsequent treatment of either condition should be taken seriously, as there could be serious consequences.
If you experience any symptoms and are looking for a good diagnosis or cure for obstetrics and gynaecology, visit us at Shri Balaji Action Medical Institute, which will provide you with the best options.